The Global energy landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. As demand for renewable energy and electric mobility accelerates, the limitations of conventional lithium‑ion batteries—cost, resource scarcity, and recycling challenges—are becoming increasingly apparent. Enter the high‑power aluminum‑ion battery, a technology that could redefine how we store and use energy.
What Are Aluminum‑Ion Batteries?
Aluminum‑ion batteries use aluminum as the active material instead of lithium. In recent prototypes, researchers have combined aluminum with graphite to create aluminum‑graphite dual‑ion batteries (AGDIB).
- Aluminum as an abundant resource: Unlike lithium, aluminum is widely available and inexpensive.
- Dual‑ion chemistry: Both aluminum and graphite ions participate in charge storage, enabling high power density.
- Design‑for‑recycling approach: These batteries are easier to recycle compared to lithium‑ion counterparts.
Breakthrough Demonstrator: Fraunhofer’s INNOBATT Project
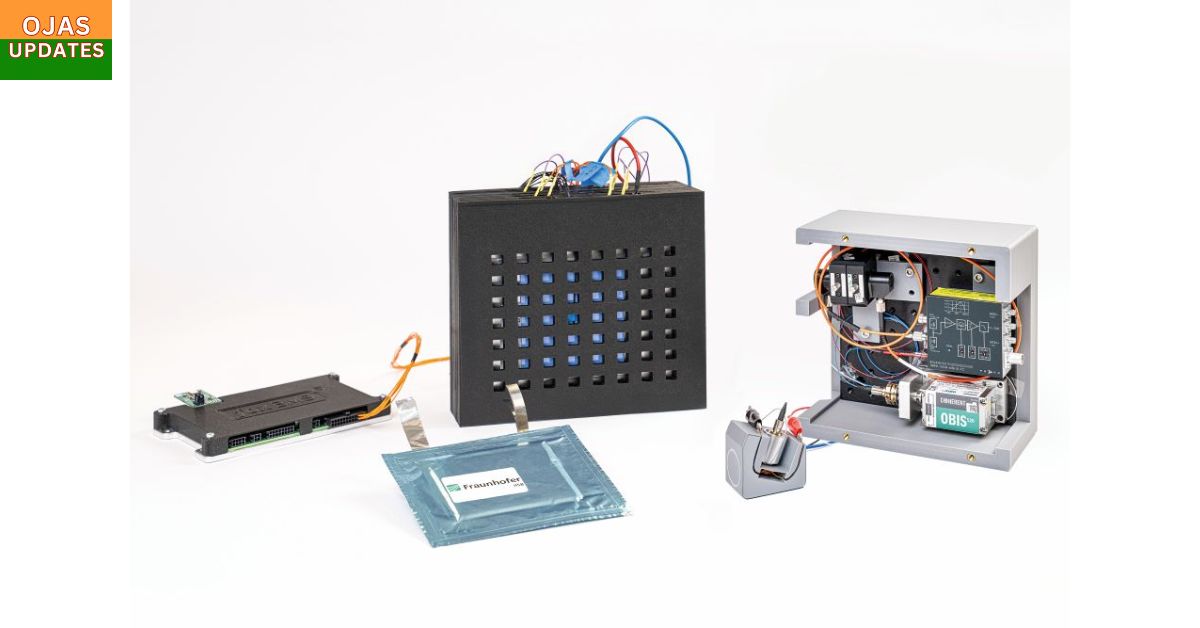
In late 2025, the Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Systems and Device Technology (IISB) unveiled the world’s first complete aluminum‑ion battery system demonstrator.
- System components: Pouch cells, battery modules, a battery management system, and even a quantum sensor.
- Performance: Demonstrated stability, fast response, and recyclability in realistic scenarios—not just lab conditions.
- Applications: Designed for dynamic grid stabilization, where rapid energy injection and absorption are critical.
This milestone proves aluminum‑ion batteries can move beyond theory into practical deployment.
Advantages Over Lithium‑Ion
Aluminum‑ion technology offers several compelling benefits:
- Cost efficiency: Aluminum is cheaper and more abundant than lithium.
- Safety: Reduced risk of thermal runaway compared to lithium‑ion.
- High power output: Ideal for applications requiring rapid charge/discharge cycles.
- Recyclability: Simplified end‑of‑life processing reduces environmental impact.
Potential Applications
While still in early stages, aluminum‑ion batteries could transform multiple sectors:
- Grid storage: Fast response makes them perfect for balancing renewable energy fluctuations.
- Electric vehicles (EVs): Future iterations may deliver the power density needed for urban mobility. Tesla has reportedly begun testing aluminum‑ion architectures for next‑gen EVs.
- Consumer electronics: Safe, recyclable batteries could power laptops, smartphones, and wearables.
- Industrial systems: High‑power applications like robotics and heavy machinery could benefit from rapid energy delivery.
Risks and Challenges
Despite their promise, aluminum‑ion batteries face hurdles:
- Energy density: Current prototypes lag behind lithium‑ion in terms of energy per kilogram.
- Scalability: Manufacturing processes must be refined for mass production.
- Market adoption: Lithium‑ion dominates the supply chain, making disruption difficult.
- Infrastructure: EV charging networks are optimized for lithium‑ion; adaptation will be required.
Why This Matters
The aluminum‑ion breakthrough is significant because it represents a lithium‑free alternative that aligns with sustainability goals. As the world pushes toward net‑zero emissions, technologies that reduce reliance on scarce resources while improving recyclability are critical.
For policymakers, aluminum‑ion batteries offer a pathway to energy independence. For consumers, they promise safer, cheaper, and greener power solutions. And for industries, they open doors to new applications where high‑power, fast‑response energy storage is essential.
Conclusion
The high‑power aluminum‑ion battery is more than a scientific curiosity—it’s a glimpse into the future of energy storage. With Fraunhofer’s demonstrator proving real‑world viability and companies like Tesla exploring aluminum‑ion for EVs, the technology is poised to challenge lithium‑ion’s dominance.
While challenges remain, the potential rewards—lower costs, improved safety, recyclability, and abundant raw materials—make aluminum‑ion batteries one of the most exciting developments in the energy sector. As 2026 unfolds, expect to hear much more about this lithium‑free revolution.